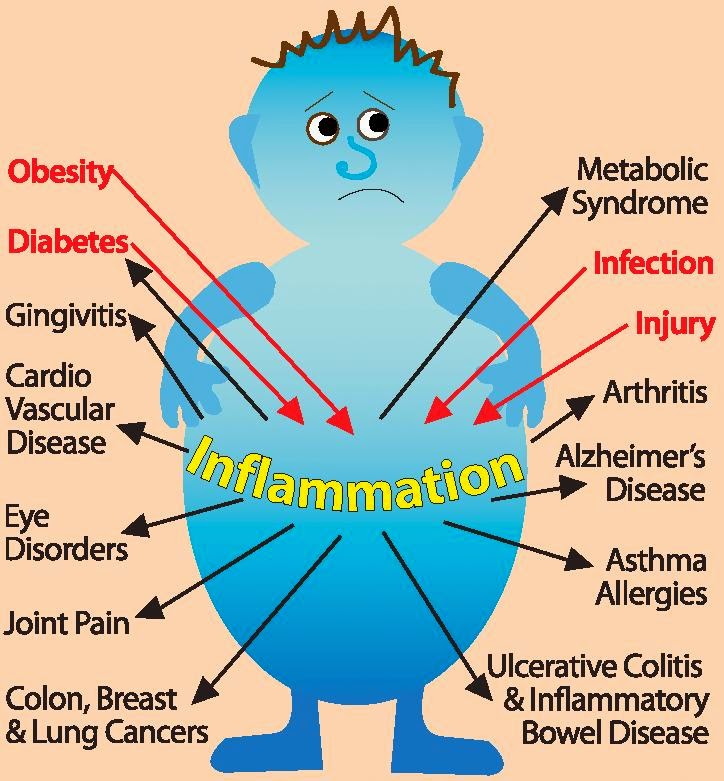
Inflammation and fatigue.
Inflammation anywhere in the body impairs the mitochondria. Why
are they so important? Mitochondria are known as “the power house of the cell”.
These organelles are the major site of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) our energy
production pathways. 90% of cellular energy is generated in the mitochondria
and if damaged from inflammation, danger signals are sent, the immune system
reacts like there are pathogens, leading to a further increase in inflammation
and oxidative stress within the body. Multiple factors can contribute to
a defect in the mitochondria such as leaky gut, poor immunity, stress,
toxicity. One way to help combat inflammation via the diet are with foods with
anti inflammatory actions. you may like to incorporate more of the following
into your diet, here’s why;
1. Fatty Fish
fresh cuts of tuna, salmon and mackerel, can be baked or boil them to keep
things healthy. Keep in mind that, while whitefish such as cod and sole are
beneficial sources of lean protein, they do not provide the same inflammation-fighting
properties as their oilier counterparts.
2. Avocado
In addition to being a great source of monounsaturated fats, avocado has the
power to reduce inflammation. It's a much healthier source of fat than killer
trans fats and goes well with many dishes. Aim for five to seven servings of
healthy fats per day, such as topping your salad with avocado, blending it into
a dressing or just eating it plain.
3. Leafy Greens
Dark leafy greens such as kale, broccoli and collards can amp up your body's inflammation-reducing
abilities. Sub in a serving or two per day.
4. Turmeric
This traditionally Indian spice is an anti-inflammatory superstar. Its
historical use in Eastern medicine has proven its use in treating a variety of
inflammatory conditions, Add a dash of it to your stir-fries or curries for an
easy dose of its inflammation-fighting properties.
5. Walnuts.
Have anti-inflammatory as well as
antioxidant properties and also possess important nutrients such as omega-3
fatty acids, copper, manganese, molybdenum and biotin. Shoot for an ounce, or
about 14 walnuts halves, every day.
6. Peppers
Both bell peppers and hot peppers provide a whole, healthy, colorful addition
to your anti-inflammatory regime. The chemical capsaicin, found in a variety of
spicy peppers, is often used in topical ointments geared toward reducing pain
and inflammation
7. Olive Oil
Aside from its raft of other health benefits, including lowering cholesterol,
olive oil helps reduce inflammation. However, studies show that only
extra-virgin olive oil obtained from the first pressing of the olives delivers
these benefits, so stick with the good stuff
8. Ginger
Ginger not only fights inflammation but also works to stop it in its tracks by
suppressing the formation of inflammatory compounds in the first place.
Gingerols, the chemicals in ginger responsible for its anti-inflammatory
properties, are reported to reduce pain and swelling
9. Beets
Brightly colored and earthy-flavored, beets provide heart and cancer protection
as well as vitamin C in addition to their power to reduce inflammation. They
taste fantastic roasted, boiled and grated raw on salads
10. Holy Basil
Look for it at specialty or Asian food
stores, where it may also be labeled as tulsi or hot basil. Use
it as you regularly would, but expect a kick.
Introducing foods that
fight inflammation into your
diet doesn't need to be difficult or stressful. Hopefully this list of whole
foods will expand your grocery list and your health opportunities all at once.